
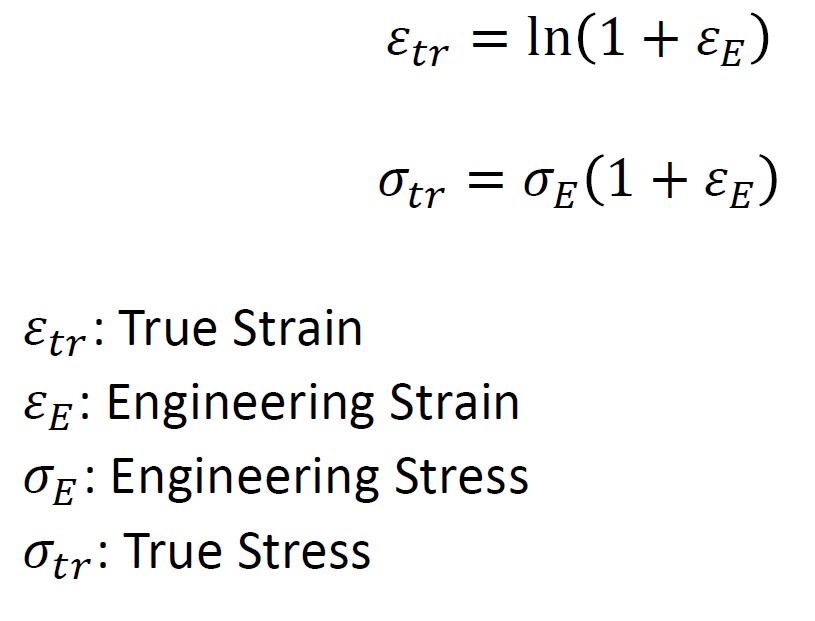
Substituting this last relation into equation (1) and solving for Stress concrete leads to a relation as follows. Total true strain is ln(L/L 0) prior to necking. The instantaneous true strain increment is -dA/A, or dL/L prior to necking. The true stress is based on the instantaneous cross section A, so that load/A. Thus, the Engineering Stress which is based on the original area decreases beyond the Ultimate Tensile Strength, whereas the True Stress increases, due to the necking or reduction of area that occurs to the specimen cross section. Engineering Stress is a measure for the applied force during tensile testing, rather than the actual stress. strain relationship Structural analysis and design requires understanding of the system of the applied forces and the material behavior The behavior of a material can be studied by means of mechanical testing Stress vs. Considering that Elastic Modulus Stress / Strain, equation (2) yields a relation between the stress and elasticity of both materials. The plastic behavior in a uni-axial tensile test can be represented as the true stress-strain curve.
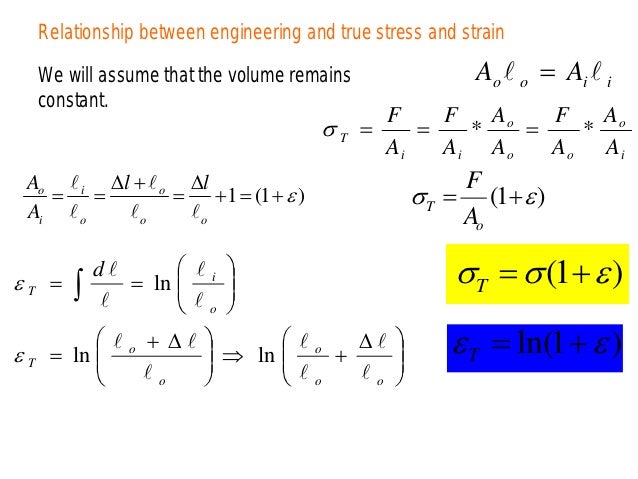
When a ductile material is loaded beyond its Ultimate Tensile Strength, necking occurs and the cross sectional area and applied force both decrease. True Stress (TS) is equivalent to the applied uniaxial tensile or compressive force at time, i divided by the cross sectional area of the specimen at time, i.Ī i = Cross Sectional Area of Specimen at time, iĭuctile materials undergo plastic deformation prior to rupture or break. by the determined equation, and the estimated engineering stress-strain curves. Stress is the internal force (per unit area) associated. Stress is defined as, the deformation force per unit area of the body or material. Engineering Stress (ES) is equivalent to the applied uniaxial tensile or compressive force at time, i divided by the original cross sectional area of the specimen.Ī o = Original Cross Sectional Area of Specimen After necking, a true stress-strain equation is determined by iteratively. Stress and Strain Definition: In engineering, stress has been defined is: when an external force applied to the object (made of an elastic material), they produce a change in shape and size of the object.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
